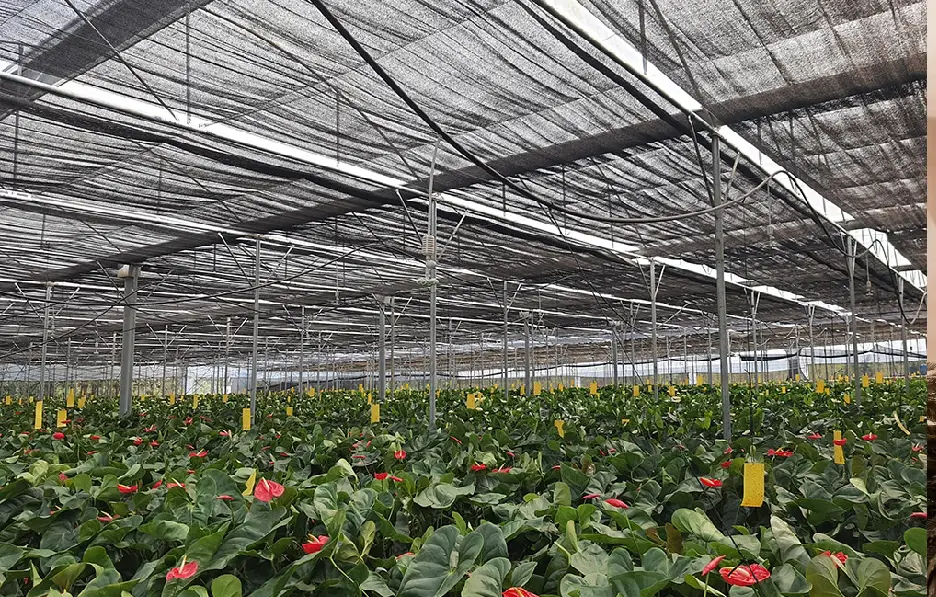
Shading your greenhouse is really important for growing healthy plants. Too much sun and heat can harm the plants inside. When you shade a greenhouse, it keeps it cooler and stops too much water from evaporating. This helps the plants grow better. In places like the Middle East and Africa, where it’s really hot and dry, it could be more important to shade greenhouses.
In this article, we’re going to talk about different ways you can use to shade your greenhouse, whether it is a portable greenhouse or a big-scale commercial greenhouse. Keep reading to learn about the different ways to shade your greenhouse.
The Basic Principles and Benefits of Shading a Greenhouse
Shading a greenhouse involves using physical barriers to reduce direct sunlight exposure inside, thereby controlling temperature and light intensity. Without shading, greenhouses can quickly overheat under strong sunlight, affecting normal plant growth and possibly causing heat damage and excessive water evaporation. Shaded greenhouses effectively lower these risks and provide more balanced light conditions for photosynthesis.
Shading offers significant benefits for plant growth, energy savings, and environmental control.
- It reduces dependency on cooling equipment by lowering internal temperatures and cutting energy use and operational costs. Proper shading also reduces water evaporation, lowering irrigation needs, crucial in arid areas.
- From a plant growth perspective, shading creates an environment with suitable light and temperature, promoting healthy growth and enhancing crop yield and quality.
- Additionally, it helps prevent pests and diseases, which often worsen in overheating and intense light conditions.
How to Shade Small Garden Greenhouses
Having explored the principles and benefits of shading, let’s examine practical shading methods for portable greenhouses. These methods are usually simple, economical, and flexible for home gardening enthusiasts under various seasonal and climatic conditions.
1. First, the use of manual shade cloths or nets.
This is an optimal choice for movable small portable greenhouses due to their simple installation and easy adjustment with seasonal and weather changes. Shade cloths and curtains effectively filter some direct sunlight, reducing the temperature inside while providing necessary diffused light for plants.
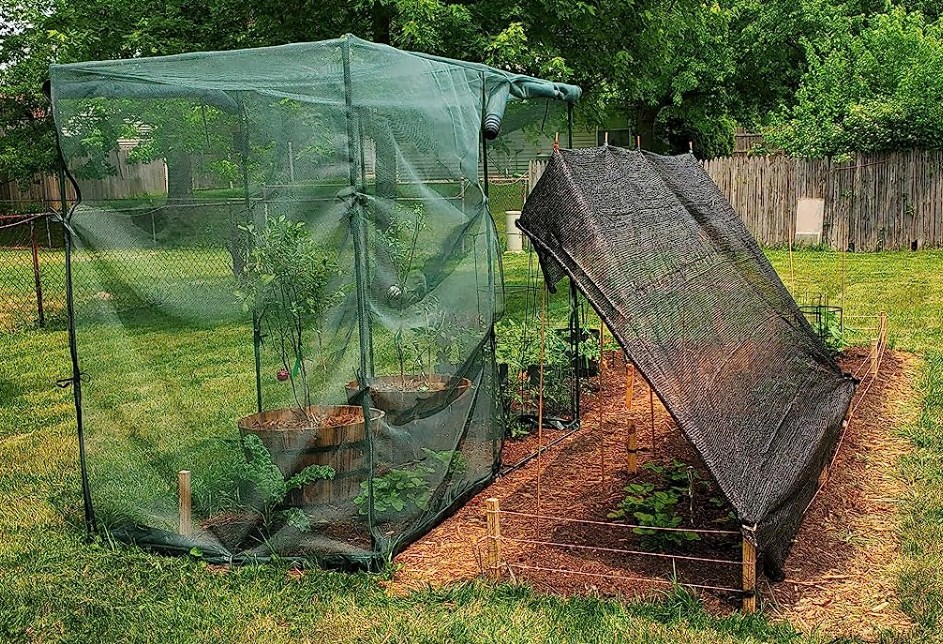

Green and black shade netting
You can choose shade nets of different colors, shade rates, and materials based on the plants you’re growing and local weather conditions, to achieve ideal shading effects.
Don’t miss: Aluminet vs. Black & White Shade Cloth: Which is better?
2. Using Greenhouse Shade Paint
In your garden greenhouses, using greenhouse shade paint is a simple and effective method. This special formula paint can be applied directly to the greenhouse’s exterior surface. This will reflect some sunlight and reduce light intensity and temperature inside. Suitable for glass or plastic greenhouses, it’s convenient to install and easy to wash off when no longer needed.

Greenhouse Shade Paint – from thorndown.co.uk
The translucency of shade paint can be adjusted according to the product, allowing gardeners to select the right shading intensity based on plant light requirements and local climate.
3. Next, external temporary shading is also effective.
If your greenhouse is very small, an existing patio umbrella might serve as a shading tool. Alternatively, with some DIY skills, you can temporarily construct a shade frame using available materials.
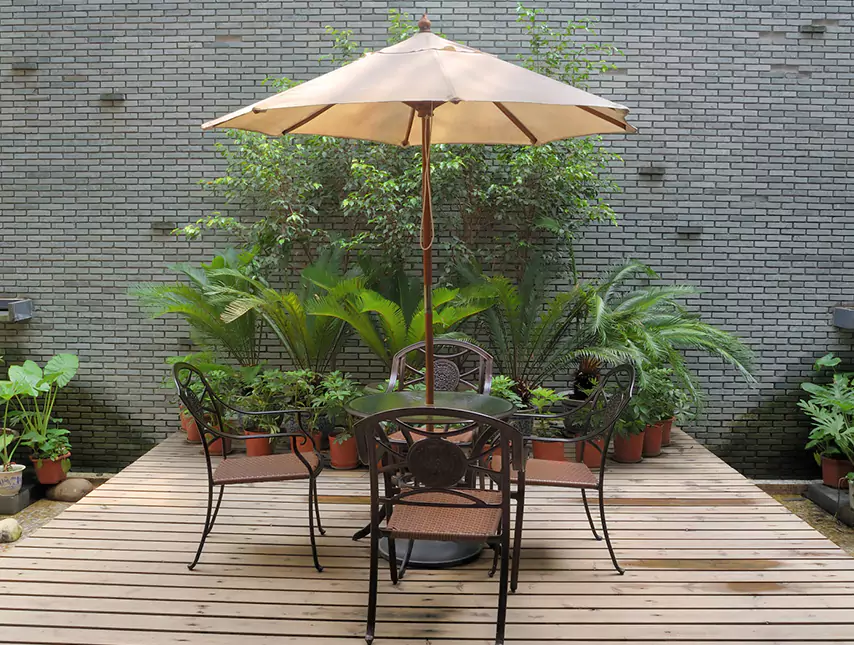

Garden Umbrell
These setups are relatively simple to install and dismantle and can be moved or adjusted according to sunlight intensity and direction, providing flexible shading solutions for greenhouses.
4. Finally, use household curtains and other internal obstructions.
If you haven’t yet bought a shade net or don’t have a large patio umbrella, this method can be an effective temporary shading solution. It’s particularly suitable for situations where long-term shading isn’t needed or as a temporary measure on days with variable weather.
How to Shade Large-Scale Commercial Greenhouses
For large industrial greenhouses, due to increased shading area and complexity, the shading needs and solutions become more intricate and advanced. In these greenhouses, shading systems not only need to control light and temperature more extensively but also integrate seamlessly with other greenhouse management systems to enhance efficiency and productivity.
1. First, automated shading systems play a key role.
These facilities usually include automated shade curtains and motorized nets that adjust shading levels automatically based on preset conditions or real-time environmental data. For instance, based on light intensity, temperature, or specific time periods, automated systems can deploy or retract shading devices. This efficient automation reduces the need for manual intervention, ensures consistency and uniformity in the greenhouse environment, and saves significant labor costs.
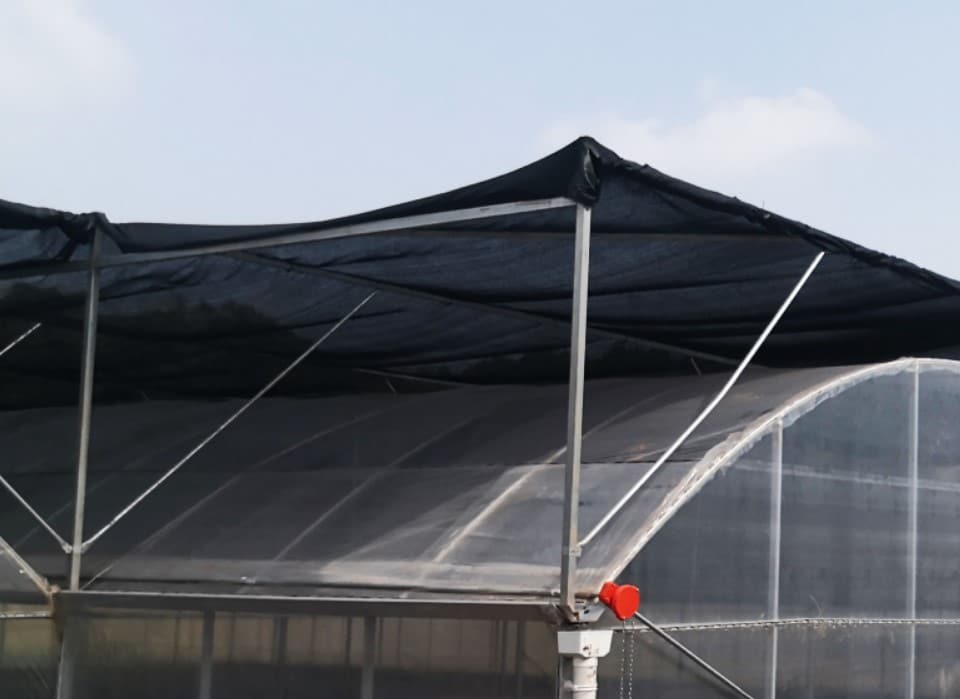

External shade system with black shade cloth
2. Second, climate control system integration is another crucial aspect.
Modern greenhouses are often equipped with advanced climate control systems that monitor and regulate temperature, humidity, light, and other environmental factors through various sensors. Integrating shading systems with these climate controls allows for more precise and dynamic environmental management. This integration helps to automatically adjust shading levels in response to external weather changes or minor variations within the internal environment, optimizing plant growth conditions and enhancing energy efficiency.
3. Lastly, the use of higher-quality shading materials is essential.
With technological advancements, new shading materials are continually emerging, offering better durability, light control capabilities, and energy efficiency. For example, our range of greenhouse shade cloths and climate screens, designed for varying shading needs, not only have upgraded, more durable materials with warranties of 4-8 years but also offer a wider choice in parameters like shading rate and light transmittance.
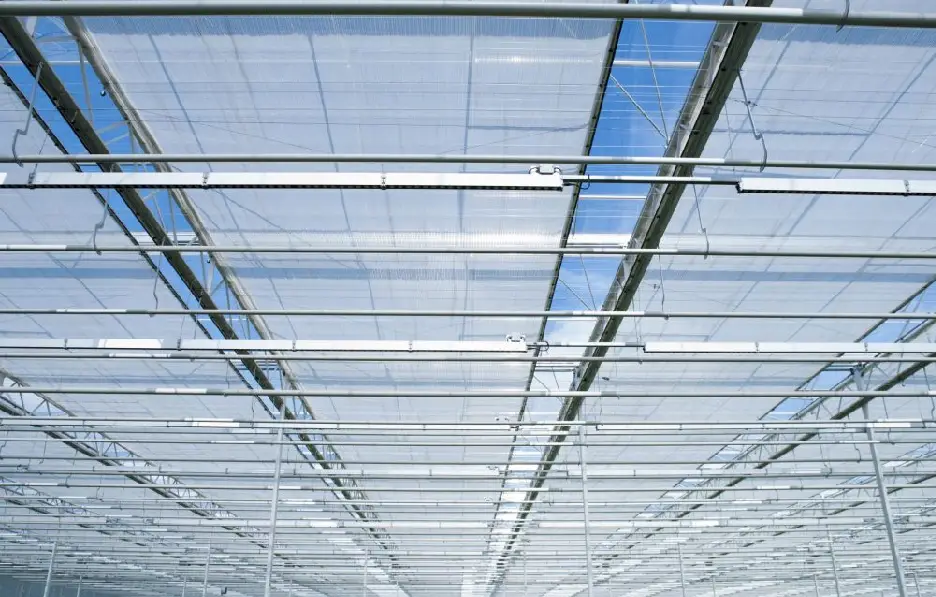

greenhouse climate thermal screen supplier
How to Choose the Right Greenhouse Shading Method?
Selecting the appropriate shading solution is crucial for ensuring the healthy growth of plants in a greenhouse. Different shading methods and materials have their strengths and weaknesses, suitable for various scenarios and needs.
1. Considering the scale of the greenhouse is key.
Family garden greenhouses, due to their smaller size, are generally more suited to simple, flexible shading methods like shade nets or temporary shade frames. For large commercial greenhouses, more efficient shading methods are needed, such as automated shading systems or high-tech solutions integrated with climate control systems. Additionally, the quality of shading nets should be durable to minimize frequent replacements.
3. The type of plants and geographic location are also important factors
Different plants have varying light requirements, so shading solutions should be adjusted according to the type of crops grown.
For instance, plants with high light demands might need shading materials with a lower shading rate, while light-sensitive plants may require higher shading materials or even light-deprived black greenhouse covering.
Double layers of greenhouse cover for light deprivation
Bonus Tip: How to Install Shade Net System?
After selecting the appropriate shading solution, correct installation and maintenance are key to ensuring long-term effectiveness and maximizing shading benefits. For small greenhouses and large-scale greenhouses, the steps and precautions for installation and maintenance differ.
1. For small portable greenhouses
The installation of shading facilities is usually straightforward. When installing shade nets or curtains, you should ensure the material is evenly laid out without wrinkles or sagging to ensure uniform shading. If using shade frames or umbrellas, determine the best position and angle based on the greenhouse’s orientation and sunlight intensity.
Consider the structure’s stability during installation, especially in windy areas, to ensure the shading facility can withstand wind. Secure the edges of the shade net properly. Also, for ease of seasonal adjustments and replacements, consider disassembly and storage in the installation process.
2. For commercial greenhouses
Regular maintenance and inspection of the shading system are necessary. The installation of shading systems is more professional. If the greenhouse is not self-designed, it typically requires the greenhouse manufacturer to install or provide guidance on-site. They will also give you training or relevant documents for routine maintenance and inspection.
Maintenance and inspection of a typical greenhouse shading system include:
- Regular lubrication and wear inspection of the motors and gear systems driving the shade curtains or nets.
- Check for damage or aging of shading materials and replace them in a timely manner to maintain shading effectiveness.
- Sensors and controllers of automated systems should also be regularly calibrated to ensure accurate response and avoid excessive shading or insufficient light due to control system failure.
- Lastly, it’s advisable to develop a regular maintenance plan and emergency response measures to deal with sudden system failures or extreme weather conditions.
Conclusion
Choosing the right shading method is crucial for both portable and large industrial greenhouses, as it significantly influences the plants’ growing environment and yield. This article has delved into various greenhouse shading techniques and their applicability to different greenhouse types.
We encourage every greenhouse manager, gardening enthusiast, and agricultural producer to thoughtfully choose the most suitable shading solution based on their unique needs and conditions. Furthermore, in hot regions, you should also consider integrating additional cooling strategies with shading can create a more conducive environment.
