Greenhouses are essential facilities for agricultural production, as they provide a controlled environment for optimal plant growth. During summer, high levels of solar radiation can lead to increased temperatures within the greenhouse, potentially harming the plants. To mitigate this issue, shade cloths (also known as shade nets or screens) have become indispensable in greenhouse management. So, how do you select the ideal shade cloth for your greenhouse?
In this article, we will explore the various types of shade cloths, their functions, and offer some tips to help you choose the best shade cloth to suit your needs.
2 Primary Shade Cloth Materials to Consider for Your Greenhouse
Shade cloths can be classified in various ways, such as by location (interior or exterior) or by purpose and function (energy-saving, shading, or both). In this discussion, we’ll focus on the two main material types: traditional knitted shade cloth and modern aluminet shade nets.
1. Knitted Shade Cloth
Knitted shade cloths are made of HDPE (high-density polyethylene) monofilament or PVA (polyvinyl alcohol formaldehyde fiber) monofilament. These cost-effective shade nets usually offer shading rates between 35% and 80%. They are mainly used for sunshade structures and exterior greenhouse shading. Under normal use, their quality assurance period is around three years.
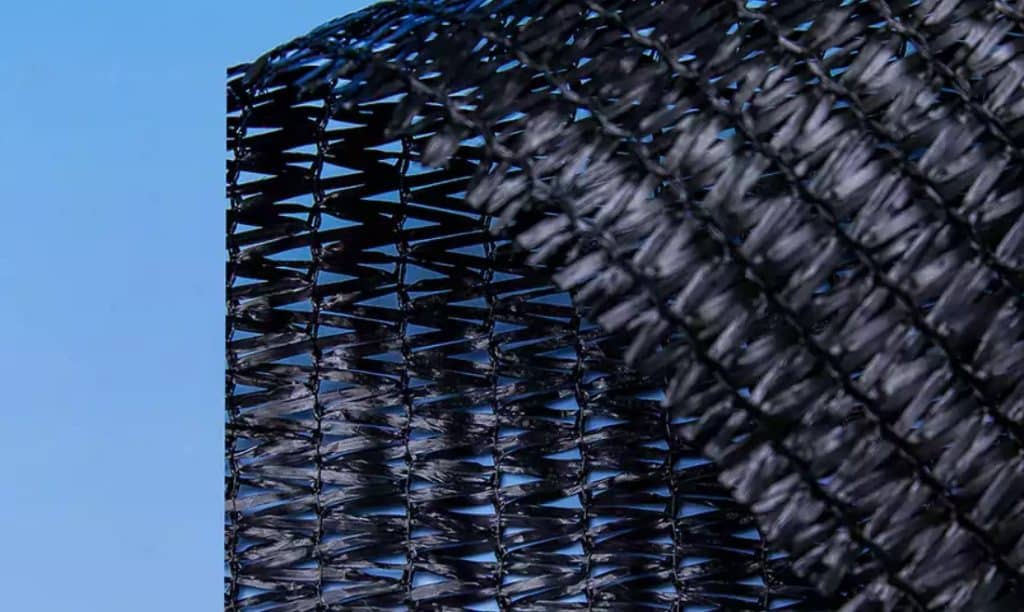

Knitted Shade Cloth for Greenhouse
2. Aluminet Shade Nets
Aluminet shade nets are comprised of aluminum foil, HDPE film, and HDPE monofilament. These shade cloths offer various advantages, including shading and cooling, water conservation and insulation, ventilation and energy conservation, anti-condensation and no dripping, and minimal shadows when retracted. Some high-end aluminet nets even include a UV protection layer that resists pollution and effectively absorbs ultraviolet rays, enhancing wear resistance.
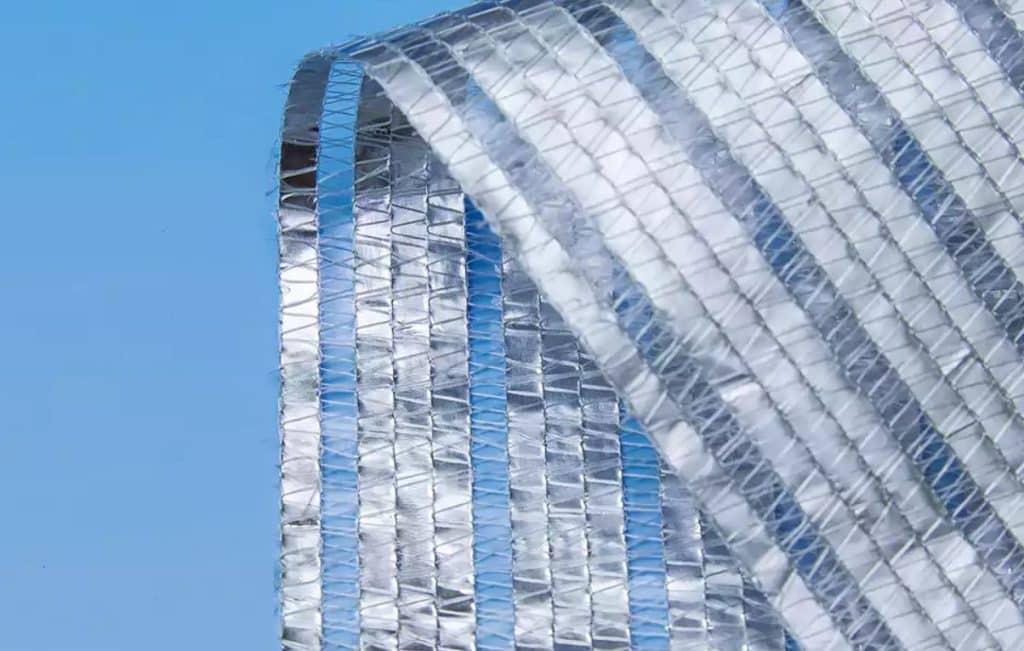

Aluminet Shade Nets for Greenhouse
Aluminet shade nets are primarily used for indoor shading and insulation in modern greenhouses, with shading rates typically ranging from 40% to 100%. Their shrinkage rate is no more than 1%, and under normal use, their quality assurance period is at least five years indoors and three years outdoors. They usually come in widths of 3.2m, 3.5m, 4.3m, 4.8m, and 5.3m, with custom lengths available upon request.
3 Key Factors to Keep in Mind When Selecting the Ideal Shade Cloth for Greenhouses
Understanding the main types of shade cloth materials used in greenhouses is important, but choosing the right one can be challenging. To make an informed decision, focus on three critical factors: shading percentage, cooling efficiency, and durability.
1. Shading Rate
To determine the appropriate shading rate for a shade net, consider the greenhouse structure, covering materials, local climate, and crop types. Keep in mind that light requirements vary among crops, and each has unique light compensation and saturation points throughout their growth stages. For instance, fungi (such as shiitake, oyster, and enoki mushrooms) require more shading than vegetables like spinach and lettuce.
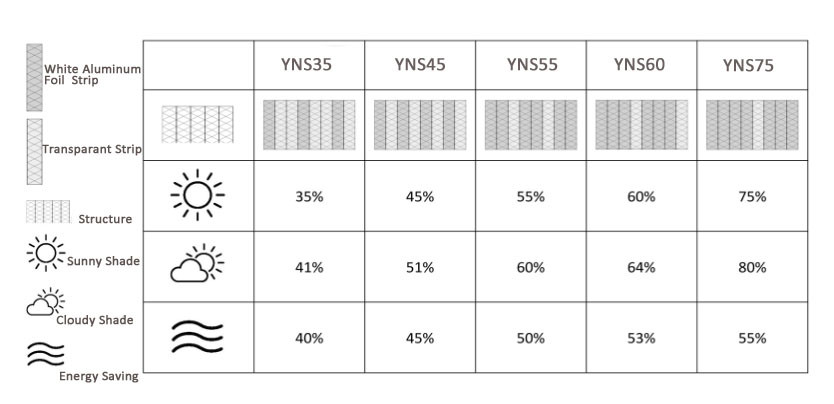
Shade Rate of INSONSHADE shade nets – YN series
By evaluating multiple factors, you can identify the most suitable light intensity for your crop and select the most cost-effective and appropriate shade net.
2. Cooling Efficiency
The shade net’s cooling efficiency improves as it reflects more solar radiation while still meeting the crop’s light requirements.
For an internal shading system, part of the reflected solar radiation is absorbed by the shade net, raising its temperature and increasing the greenhouse’s temperature through heat exchange with indoor air. To optimize indoor cooling efficiency, choose a shade net with high solar radiation reflectivity. Aluminet nets, for example, offer significantly better cooling efficiency than other types due to their higher reflectivity. Consider aluminet nets for indoor shading purposes.
For external shading systems, the cooling efficiency mainly depends on the shading rate, as the energy absorbed by the shade net itself can be disregarded.
3. Durability
A shade net’s durability is influenced by factors both inside and outside the greenhouse, including climate, temperature, ultraviolet (UV) rays, and chemicals. These elements can impact the shade net’s lifespan.
Indoor shade cloths are protected from harsh weather conditions such as wind, rain, snow, and hail, resulting in a longer lifespan compared to external ones. However, the chemicals used in greenhouses, like insecticides, fertilizers, and pesticides, can react with the UV stabilizers in the shade net’s UV layer, reducing their effectiveness. Avoid letting chemicals come into contact with indoor shade cloths.
Outdoor shade cloths are exposed to more UV rays and harsh weather conditions like wind, rain, snow, and hail. When choosing an outdoor shade cloth, consider the shade net’s strength, heat resistance, and UV resistance.
Understanding the Connection Between Greenhouse Shading Systems and Shade Cloth
Shade cloth plays an essential role in greenhouse shading systems, which can be divided into two types based on their location: exterior and interior shading systems. The choice of shading materials and their functions depends on the system’s location.
1. Exterior Shading System
Exterior shading systems are set up outside the greenhouse on the roof, blocking excess sunlight and preventing it from raising the indoor temperature. This method offers the most effective cooling. Since the shade cloth is outdoors, it doesn’t directly influence other environmental factors within the greenhouse, focusing primarily on temperature reduction and light regulation.
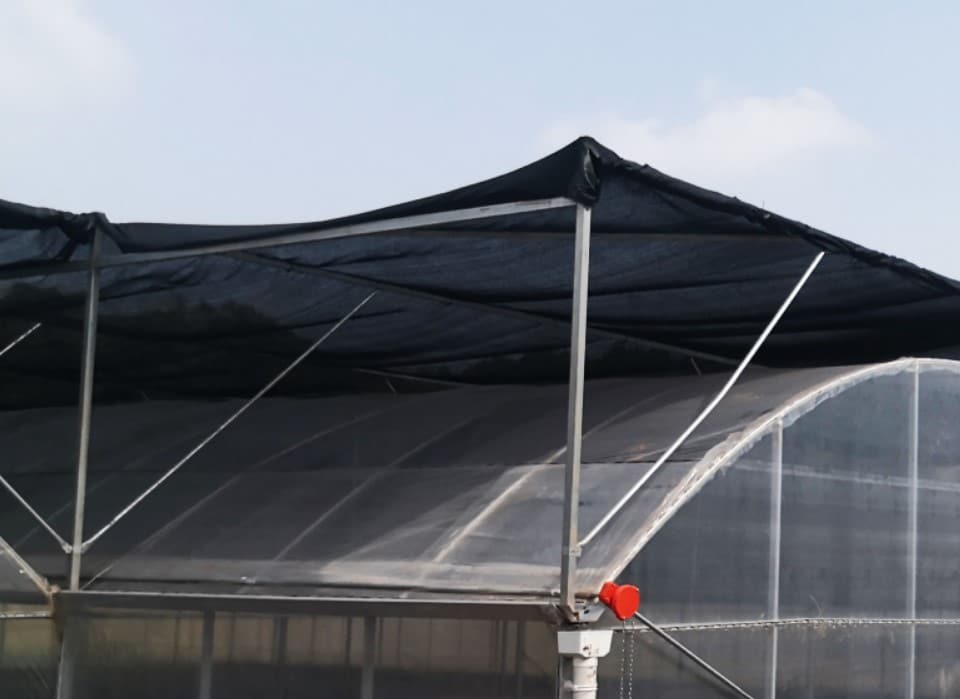

External shade system with black shade cloth
2. Interior Shading System
Interior shading systems involve installing shade cloth inside the greenhouse to manage excess sunlight. When sunlight enters the greenhouse, it is partially reflected and absorbed by the shade cloth. The reflected sunlight bounces back into the greenhouse, while the absorbed portion heats the shade cloth, which in turn transfers heat to the indoor air. Consequently, interior shading’s cooling effect is slightly less effective than exterior shading. However, when used with a wet curtain and fan cooling system, interior shading considerably boosts cooling efficiency, improving airflow and reducing the need for cooling and ventilation.
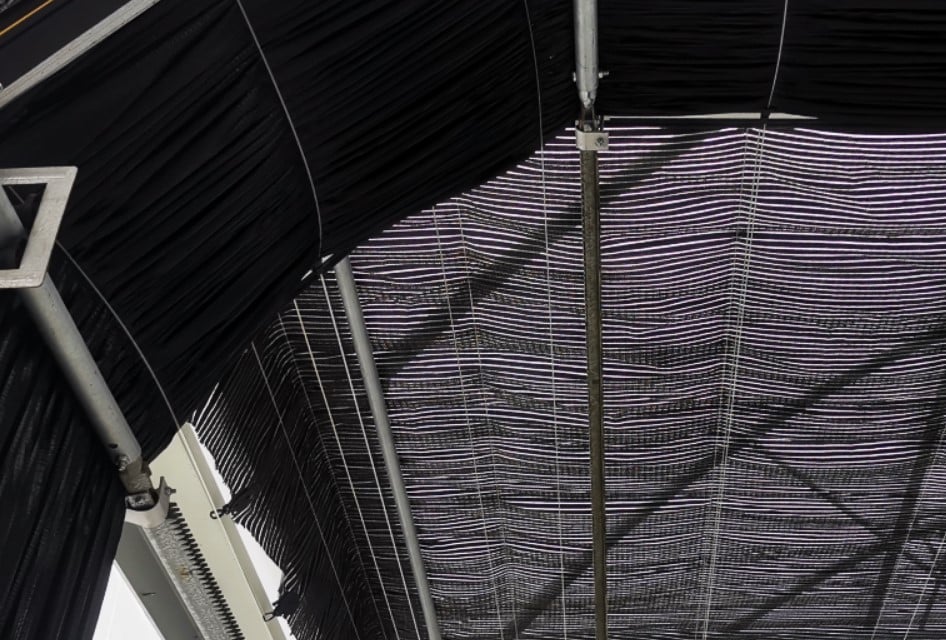

Greenhouse Interior Shading System
In modern greenhouses, selecting the right shade cloth material can provide additional benefits like thermal insulation, humidity control, and drip prevention. Aluminum foil shade cloth is popular due to its airtightness and ability to absorb and reflect far-infrared radiation, offering excellent thermal insulation. Made from moisture-absorbing polyester fibers, this shade cloth can also regulate humidity. Moreover, its higher temperature prevents condensation, and its fibers can absorb and support dripping condensation from the greenhouse covering material, significantly reducing dripping problems.
Given its many functions, interior shading is more cost-effective and practical than exterior shading, making it a more common choice for modern greenhouses.
Conclusion
Choosing the best shade cloth for your greenhouse involves considering factors such as plant requirements, climate conditions, shading effectiveness, cooling efficiency, and durability. Additionally, when selecting a shade cloth, it’s important to determine whether it will be used for interior or exterior shading to ensure optimal shading and cooling effects in different application scenarios, ultimately promoting plant growth and yield within the greenhouse.
